Beginner's Guide to Hyperfoil: part 3
In this article we’ll show how to run Hyperfoil inside an Openshift cluster, benchmarking workload within the same cluster. This assumes that you have sufficient privileges to install operators and create new namespaces (projects).
Demo workload
We will install Vehicle Market, our demo application we’ve used in the first article using console and Openshift Template.
Login into your cluster and run this:
# Fetch the default domain your cluster uses
export DOMAIN=$(oc get ingresscontrollers.operator.openshift.io \
-n openshift-ingress-operator default -o jsonpath='{ .status.domain }')
oc new-project vehicle-market
curl -Ls http://vehicle-market-template.hyperfoil.io | \
oc process -f - -p DOMAIN=vehicle-market.$DOMAIN | oc apply -f -
echo http://vehicle-market.$DOMAIN
This will deploy 5 pods, 5 services and 4 routes in the vehicle-market namespace, and load some example data. You can open the URL printed as the last line in your browser and explore the application.
Installing Hyperfoil
You can install Hyperfoil Operator either through web-console, or on command-line using oc. For the web-console installation switch to the ‘Administrator view’ and go to Operators/OperatorHub. Filter ‘Hyperfoil’ and you should see the operator:
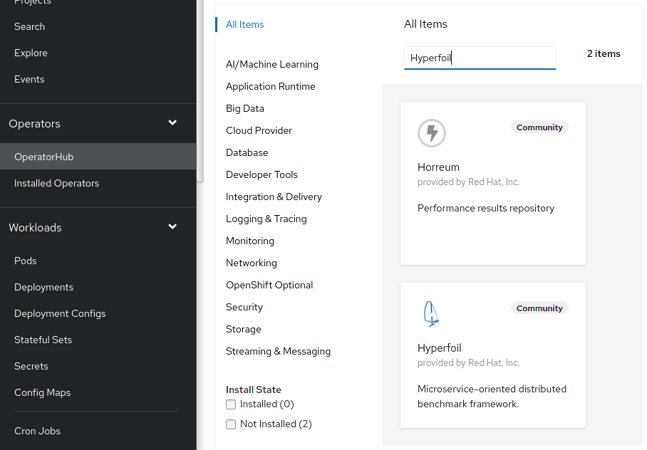
Click on Hyperfoil and go through the wizard with all settings on default values (install to all namespaces with automatic approval).
Alternatively you can create the subscription by defining this subscription:
apiVersion: operators.coreos.com/v1alpha1
kind: Subscription
metadata:
name: hyperfoil-operator
namespace: openshift-operators
spec:
channel: alpha
name: hyperfoil-bundle
source: community-operators
sourceNamespace: openshift-marketplace
In any case you should end up with Hyperfoil listed amongst the installed operators:
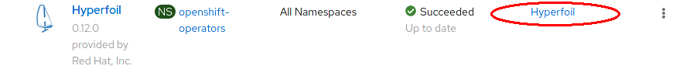
Now you can create a new namespace for Hyperfoil and add the custom resource. In web-console open the dropdown on top and create a new namespace hyperfoil. When the page reloads with all operators (that can take a couple of seconds) click on ‘Hyperfoil’ in the Provided APIs column (highlighted with red ellipse above). Press the ‘Create Hyperfoil’ button on the right side and switch to YAML View, filling the definition below and push ‘Create’ button below the editor.
apiVersion: hyperfoil.io/v1alpha2
kind: Hyperfoil
metadata:
name: hyperfoil
spec:
route:
host: hyperfoil.apps.your.domain.com
The only non-default value in this example is the hostname for the route; default hostname would be probably a bit longer. By default the route uses edge termination (the TLS connection is terminated at the router, the communication inside cluster is not encrypted). Therefore we will be connecting to port 443.
On command line just use commands below, passing the CR above as hyperfoil.yaml.
$ oc new-project hyperfoil
$ oc apply -f hyperfoil.yaml
$ oc get hf
NAME VERSION ROUTE PVC STATUS
hyperfoil hyperfoil.apps.your.domain.com Ready
Using Hyperfoil
Now it’s time to open CLI as we’ve done in the previous articles:
export VMB=$HOME/vehicle-market/benchmarks
podman run -it --rm -v $VMB:/benchmarks:Z -v /tmp/reports:/tmp/reports:Z \
--network=host quay.io/hyperfoil/hyperfoil cli
```sh [hyperfoil]$ connect hyperfoil.apps.your.domain.com:443 ERROR: javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: Failed to create SSL connection: Failed to create SSL connection: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target: unable to find valid certification path to requested target Hint: TLS certificate verification might have failed. Use --insecure to disable validation. Failed connecting to hyperfoil.apps.your.domain.com:443 ```
We are connecting to the route on port 443 (you could also use connect https://hyperfoil.apps.your.domain.com or connect hyperfoi.apps.your.domain.com -p 443) but the certificate issued by the router might not be valid if this is not a production cluster. Use --insecure (or -k) in that case:
[hyperfoil]$ connect hyperfoil.apps.ocp.scalelab:443 -k
WARNING: Hyperfoil TLS certificate validity is not checked. Your credentials might get compromised.
Connected!
[hyperfoil@hyperfoil]$ upload /benchmarks/first-benchmark.hf.yaml
Loaded benchmark first-benchmark, uploading...
... done.
[hyperfoil@hyperfoil]$ run
ERROR: Server responded with unexpected code: 403, Forbidden:
Server is started in clustered mode; benchmarks must define agents.
Failed to start benchmark first-benchmark
Oops, what happened now? We have tried to execute the benchmark from Part 1 that worked just fine when executed from start-local. The controller in Openshift is started in a clustered mode, though, and single-vm runs are prohibited. We need to tell Hyperfoil to run this benchmark using an agent - and the controller will spin up another pod that will fire the load.
name: clustered-benchmark
agents:
agent-one:
agent-two:
http:
host: http://vehicle-market.apps.your.domain.com
sharedConnections: 10
usersPerSec: 10
duration: 120s
scenario:
- fetchIndex:
- httpRequest:
GET: /
Besides adding the agents (with empty definition) we have corrected the endpoint hostname and increased duration to 2 minutes. While the benchmark is running you can verify that controller created another pod:
$ oc get pods -n hyperfoil
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
agent-0001-agent-one 1/1 Running 0 13s
agent-0001-agent-two 1/1 Running 0 13s
hyperfoil-controller 1/1 Running 0 17m
Both the sharedConnections and usersPerSec have been evenly distributed between the two agents; each will use 5 connections and run 5 users per second.
See the agents section documentation for further customization of the agents.
Configuration options such as securing the controller with password, persistence, logging, hooks etc. can be found in the installation guide.
WebCLI
You are already familiar with Hyperfoil CLI but starting it up in Podman might not be the most convenient way (and neither is keeping Hyperfoil distribution locally). There’s an easy solution for that: just use your browser. Since Hyperfoil 0.14 the controller exposes a CLI — let’s navigate to https://hyperfoil.apps.your.domain.com:
This CLI is automatically connected to the controller where it is running and cannot connect to any other controller (the command connect is missing, as well as exit and few other ones). Some commands are altered, e.g. upload cannot accept path on your machine while in browser — type just upload and then press a button that lets you select the benchmark file. edit does not open vi/vim/your favorite editor but displays a Monaco editor inside the browser. export and report cannot take --destination, instead these commands open download dialogue in the browser.
Tips and tricks
http://vehicle-market.apps.your.domain.com is probably resolved to the load balancer that routes the traffic even before Openshift Ingresses. You might want to bypass this component, hitting the Ingresses directly. You can do that by setting addresses for the endpoints manually:
$ oc get po -n openshift-ingress -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
router-default-56b959876c-94x2f 1/1 Running 1 60d 192.168.222.19 worker006 <none> <none>
router-default-56b959876c-9tqvb 1/1 Running 0 60d 192.168.222.22 worker009 <none> <none>
http:
host: http://vehicle-market.apps.your.domain.com
sharedConnections: 10
addresses:
- 192.168.222.19
- 192.168.222.22
The connections will be randomly assigned to one of those IPs. You can also use bypass ingress completely and target the service directly - addresses can use hostnames and customize the actual port as well:
http:
host: http://vehicle-market.apps.your.domain.com
sharedConnections: 10
addresses:
- frontend.vehicle-market.svc.cluster.local:8080